There is the list of 300 core Java interview questions. If there is any core Java interview question that has been asked to you, kindly post it in the ask question section. We assure that you will get here the 90% frequently asked interview questions and answers.
The answers to the Core Java interview questions are short and to the point. The core Java interview questions are categorized in Basics of Java interview questions, OOPs interview questions, String Handling interview questions, Multithreading interview questions, collection interview questions, JDBC interview questions, etc.
Java is the high-level, object-oriented, robust, secure programming language, platform-independent, high performance, Multithreaded, and portable programming language. It was developed by James Gosling in June 1991. It can also be known as the platform as it provides its own JRE and API.
The differences between C++ and Java are given in the following table.
| Comparison Index | C++ | Java |
|---|---|---|
| Platform-independent | C++ is platform-dependent. | Java is platform-independent. |
| Mainly used for | C++ is mainly used for system programming. | Java is mainly used for application programming. It is widely used in window, web-based, enterprise and mobile applications. |
| Design Goal | C++ was designed for systems and applications programming. It was an extension of C programming language. | Java was designed and created as an interpreter for printing systems but later extended as a support network computing. It was designed with a goal of being easy to use and accessible to a broader audience. |
| Goto | C++ supports the goto statement. | Java doesn't support the goto statement. |
| Multiple inheritance | C++ supports multiple inheritance. | Java doesn't support multiple inheritance through class. It can be achieved by interfaces in java. |
| Operator Overloading | C++ supports operator overloading. | Java doesn't support operator overloading. |
| Pointers | C++ supports pointers. You can write pointer program in C++. | Java supports pointer internally. However, you can't write the pointer program in java. It means java has restricted pointer support in Java. |
| Compiler and Interpreter | C++ uses compiler only. C++ is compiled and run using the compiler which converts source code into machine code so, C++ is platform dependent. | Java uses compiler and interpreter both. Java source code is converted into bytecode at compilation time. The interpreter executes this bytecode at runtime and produces output. Java is interpreted that is why it is platform independent. |
| Call by Value and Call by reference | C++ supports both call by value and call by reference. | Java supports call by value only. There is no call by reference in java. |
| Structure and Union | C++ supports structures and unions. | Java doesn't support structures and unions. |
| Thread Support | C++ doesn't have built-in support for threads. It relies on third-party libraries for thread support. | Java has built-in thread support. |
| Documentation comment | C++ doesn't support documentation comment. | Java supports documentation comment (/** . */) to create documentation for java source code. |
| Virtual Keyword | C++ supports virtual keyword so that we can decide whether or not override a function. | Java has no virtual keyword. We can override all non-static methods by default. In other words, non-static methods are virtual by default. |
| unsigned right shift >>> | C++ doesn't support >>> operator. | Java supports unsigned right shift >>> operator that fills zero at the top for the negative numbers. For positive numbers, it works same like >> operator. |
| Inheritance Tree | C++ creates a new inheritance tree always. | Java uses a single inheritance tree always because all classes are the child of Object class in java. The object class is the root of the inheritance tree in java. |
| Hardware | C++ is nearer to hardware. | Java is not so interactive with hardware. |
| Object-oriented | C++ is an object-oriented language. However, in C language, single root hierarchy is not possible. | Java is also an object-oriented language. However, everything (except fundamental types) is an object in Java. It is a single root hierarchy as everything gets derived from java.lang.Object. |
There are the following features in Java Programming Language.
Java Virtual Machine is a virtual machine that enables the computer to run the Java program. JVM acts like a run-time engine which calls the main method present in the Java code. JVM is the specification which must be implemented in the computer system. The Java code is compiled by JVM to be a Bytecode which is machine independent and close to the native code.
JVM is an acronym for Java Virtual Machine; it is an abstract machine which provides the runtime environment in which Java bytecode can be executed. It is a specification which specifies the working of Java Virtual Machine. Its implementation has been provided by Oracle and other companies. Its implementation is known as JRE.
JVMs are available for many hardware and software platforms (so JVM is platform dependent). It is a runtime instance which is created when we run the Java class. There are three notions of the JVM: specification, implementation, and instance.
JRE stands for Java Runtime Environment. It is the implementation of JVM. The Java Runtime Environment is a set of software tools which are used for developing Java applications. It is used to provide the runtime environment. It is the implementation of JVM. It physically exists. It contains a set of libraries + other files that JVM uses at runtime.
JDK is an acronym for Java Development Kit. It is a software development environment which is used to develop Java applications and applets. It physically exists. It contains JRE + development tools. JDK is an implementation of any one of the below given Java Platforms released by Oracle Corporation:
Just-In-Time(JIT) compiler: It is used to improve the performance. JIT compiles parts of the bytecode that have similar functionality at the same time, and hence reduces the amount of time needed for compilation. Here the term “compiler” refers to a translator from the instruction set of a Java virtual machine (JVM) to the instruction set of a specific CPU.
A platform is the hardware or software environment in which a piece of software is executed. There are two types of platforms, software-based and hardware-based. Java provides the software-based platform.
There are the following differences between the Java platform and other platforms.
The bytecode. Java compiler converts the Java programs into the class file (Byte Code) which is the intermediate language between source code and machine code. This bytecode is not platform specific and can be executed on any computer.
Classloader is a subsystem of JVM which is used to load class files. Whenever we run the java program, it is loaded first by the classloader. There are three built-in classloaders in Java.
Yes, Java allows to save our java file by .java only, we need to compile it by javac .java and run by java classname Let's take a simple example:
compile it by javac .java
run it by java A
It is empty, but not null.
The program compiles and runs correctly because the order of specifiers doesn't matter in Java.
The local variables are not initialized to any default value, neither primitives nor object references.
In Java, access specifiers are the keywords which are used to define the access scope of the method, class, or a variable. In Java, there are four access specifiers given below.
The methods or variables defined as static are shared among all the objects of the class. The static is the part of the class and not of the object. The static variables are stored in the class area, and we do not need to create the object to access such variables. Therefore, static is used in the case, where we need to define variables or methods which are common to all the objects of the class.
For example, In the class simulating the collection of the students in a college, the name of the college is the common attribute to all the students. Therefore, the college name will be defined as static.
There are various advantages of defining packages in Java.
The output of the above code will be
30Javatpoint Javatpoint1020
Explanation
In the first case, 10 and 20 are treated as numbers and added to be 30. Now, their sum 30 is treated as the string and concatenated with the string Javatpoint. Therefore, the output will be 30Javatpoint.
In the second case, the string Javatpoint is concatenated with 10 to be the string Javatpoint10 which will then be concatenated with 20 to be Javatpoint1020.
The output of the above code will be
200Javatpoint Javatpoint200
Explanation
In the first case, The numbers 10 and 20 will be multiplied first and then the result 200 is treated as the string and concatenated with the string Javatpoint to produce the output 200Javatpoint.
In the second case, The numbers 10 and 20 will be multiplied first to be 200 because the precedence of the multiplication is higher than addition. The result 200 will be treated as the string and concatenated with the string Javatpointto produce the output as Javatpoint200.
The above code will give the compile-time error because the for loop demands a boolean value in the second part and we are providing an integer value, i.e., 0.
There is given more than 50 OOPs (Object-Oriented Programming and System) interview questions. However, they have been categorized in many sections such as constructor interview questions, static interview questions, Inheritance Interview questions, Abstraction interview question, Polymorphism interview questions, etc. for better understanding.
It is a programming paradigm based on objects having data and methods defined in the class to which it belongs. Object-oriented paradigm aims to incorporate the advantages of modularity and reusability. Objects are the instances of classes which interacts with one another to design applications and programs. There are the following features of the object-oriented paradigm.
The Object is the real-time entity having some state and behavior. In Java, Object is an instance of the class having the instance variables as the state of the object and the methods as the behavior of the object. The object of a class can be created by using the new keyword.
There are the following basic differences between the object-oriented language and object-based language.
All object references are initialized to null in Java.
The constructor can be defined as the special type of method that is used to initialize the state of an object. It is invoked when the class is instantiated, and the memory is allocated for the object. Every time, an object is created using the new keyword, the default constructor of the class is called. The name of the constructor must be similar to the class name. The constructor must not have an explicit return type.
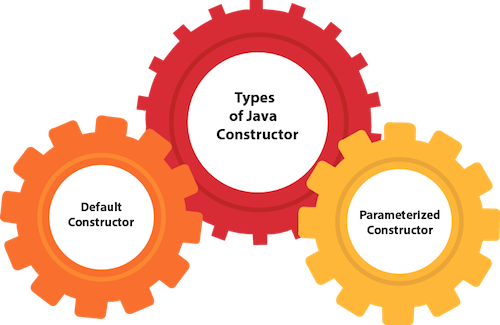
Based on the parameters passed in the constructors, there are two types of constructors in Java.

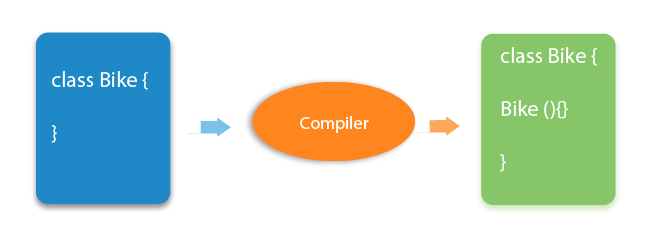
The purpose of the default constructor is to assign the default value to the objects. The java compiler creates a default constructor implicitly if there is no constructor in the class.
0 null 0 null
Explanation: In the above class, you are not creating any constructor, so compiler provides you a default constructor. Here 0 and null values are provided by default constructor.
More Details.
Ans: yes, The constructor implicitly returns the current instance of the class (You can't use an explicit return type with the constructor). More Details.
No, The constructor is not inherited.
No, the constructor can't be final.
Yes, the constructors can be overloaded by changing the number of arguments accepted by the constructor or by changing the data type of the parameters. Consider the following example.
In the above program, The constructor Test is overloaded with another constructor. In the first call to the constructor, The constructor with one argument is called, and i will be initialized with the value 10. However, In the second call to the constructor, The constructor with the 2 arguments is called, and i will be initialized with the value 15.
There is no copy constructor in java. However, we can copy the values from one object to another like copy constructor in C++.
There are many ways to copy the values of one object into another in java. They are:
In this example, we are going to copy the values of one object into another using java constructor.
111 Karan 111 Karan
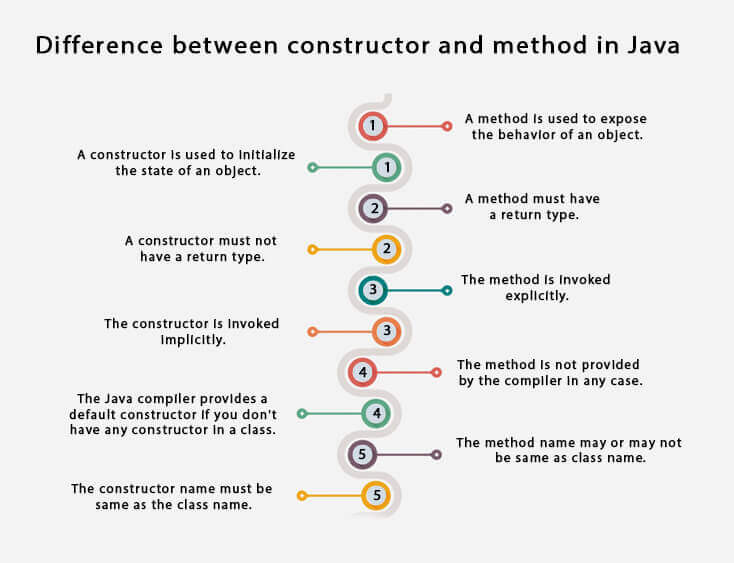
There are many differences between constructors and methods. They are given below.
| Java Constructor | Java Method |
|---|---|
| A constructor is used to initialize the state of an object. | A method is used to expose the behavior of an object. |
| A constructor must not have a return type. | A method must have a return type. |
| The constructor is invoked implicitly. | The method is invoked explicitly. |
| The Java compiler provides a default constructor if you don't have any constructor in a class. | The method is not provided by the compiler in any case. |
| The constructor name must be same as the class name. | The method name may or may not be same as class name. |
The output of the program is 0 because the variable i is initialized to 0 internally. As we know that a default constructor is invoked implicitly if there is no constructor in the class, the variable i is initialized to 0 since there is no constructor in the class.
There is a compiler error in the program because there is a call to the default constructor in the main method which is not present in the class. However, there is only one parameterized constructor in the class Test. Therefore, no default constructor is invoked by the constructor implicitly.
The static variable is used to refer to the common property of all objects (that is not unique for each object), e.g., The company name of employees, college name of students, etc. Static variable gets memory only once in the class area at the time of class loading. Using a static variable makes your program more memory efficient (it saves memory). Static variable belongs to the class rather than the object.
Output:111 Karan ITS 222 Aryan ITS
More Details.
Two main restrictions are applied to the static methods.
Because the object is not required to call the static method. If we make the main method non-static, JVM will have to create its object first and then call main() method which will lead to the extra memory allocation. More Details.
No, we can't override static methods.
Static block is used to initialize the static data member. It is executed before the main method, at the time of classloading.
Output: static block is invoked Hello main
Ans) No, It was possible before JDK 1.7 using the static block. Since JDK 1.7, it is not possible. More Details.
Program compiles. However, at runtime, It throws an error "NoSuchMethodError."
| static or class method | instance method |
|---|---|
| 1)A method that is declared as static is known as the static method. | A method that is not declared as static is known as the instance method. |
| 2)We don't need to create the objects to call the static methods. | The object is required to call the instance methods. |
| 3)Non-static (instance) members cannot be accessed in the static context (static method, static block, and static nested class) directly. | Static and non-static variables both can be accessed in instance methods. |
| 4)For example: public static int cube(int n) | For example: public void msg(). |
As we know that the static context (method, block, or variable) belongs to the class, not the object. Since Constructors are invoked only when the object is created, there is no sense to make the constructors static. However, if you try to do so, the compiler will show the compiler error.
In Java, if we make the abstract methods static, It will become the part of the class, and we can directly call it which is unnecessary. Calling an undefined method is completely useless therefore it is not allowed.
Yes, we can declare static variables and methods in an abstract method. As we know that there is no requirement to make the object to access the static context, therefore, we can access the static context declared inside the abstract class by using the name of the abstract class. Consider the following example.
Output
Test.java:5: error: cannot assign a value to final variable this this = null; ^ 1 error
Yes, It is possible to use this keyword to refer static members because this is just a reference variable which refers to the current class object. However, as we know that, it is unnecessary to access static variables through objects, therefore, it is not the best practice to use this to refer static members. Consider the following example.
Output
Constructor chaining enables us to call one constructor from another constructor of the class with respect to the current class object. We can use this keyword to perform constructor chaining within the same class. Consider the following example which illustrates how can we use this keyword to achieve constructor chaining.
Output
ID: 105 Name:Vikas age:22 address: Delhi
As we know, that this refers to the current class object, therefore, it must be similar to the current class object. However, there can be two main advantages of passing this into a method instead of the current class object.
Inheritance is a mechanism by which one object acquires all the properties and behavior of another object of another class. It is used for Code Reusability and Method Overriding. The idea behind inheritance in Java is that you can create new classes that are built upon existing classes. When you inherit from an existing class, you can reuse methods and fields of the parent class. Moreover, you can add new methods and fields in your current class also. Inheritance represents the IS-A relationship which is also known as a parent-child relationship.
There are five types of inheritance in Java.
Multiple inheritance is not supported in Java through class.
There are various advantages of using inheritance in Java that is given below.
The object class is the superclass of all other classes in Java.
To reduce the complexity and simplify the language, multiple inheritance is not supported in java. Consider a scenario where A, B, and C are three classes. The C class inherits A and B classes. If A and B classes have the same method and you call it from child class object, there will be ambiguity to call the method of A or B class.
Since the compile-time errors are better than runtime errors, Java renders compile-time error if you inherit 2 classes. So whether you have the same method or different, there will be a compile time error.
Compile Time Error
Aggregation can be defined as the relationship between two classes where the aggregate class contains a reference to the class it owns. Aggregation is best described as a has-a relationship. For example, The aggregate class Employee having various fields such as age, name, and salary also contains an object of Address class having various fields such as Address-Line 1, City, State, and pin-code. In other words, we can say that Employee (class) has an object of Address class. Consider the following example.
Address.java
Employee.java
Output
111 varun gzb UP india 112 arun gno UP india
Holding the reference of a class within some other class is known as composition. When an object contains the other object, if the contained object cannot exist without the existence of container object, then it is called composition. In other words, we can say that composition is the particular case of aggregation which represents a stronger relationship between two objects. Example: A class contains students. A student cannot exist without a class. There exists composition between class and students.
Aggregation represents the weak relationship whereas composition represents the strong relationship. For example, the bike has an indicator (aggregation), but the bike has an engine (composition).
The pointer is a variable that refers to the memory address. They are not used in Java because they are unsafe(unsecured) and complex to understand.
The super keyword in Java is a reference variable that is used to refer to the immediate parent class object. Whenever you create the instance of the subclass, an instance of the parent class is created implicitly which is referred by super reference variable. The super() is called in the class constructor implicitly by the compiler if there is no super or this.
animal is created dog is created